エンタープライズクラウド部の松田です。こんにちは。
今回はパーティションを活用して、マルチアカウント環境における、AWS CloudTrailログの検索を高速化する方法をご紹介します。
1. はじめに
Amazon Athenaを使用して、AWSマネジメントコンソールへのサインインログを抽出するという機会がありました。クエリ高速化のために、アカウントID・AWSリージョン・日付をキーとしてパーティション分割してみましたので、備忘として残しておきます。
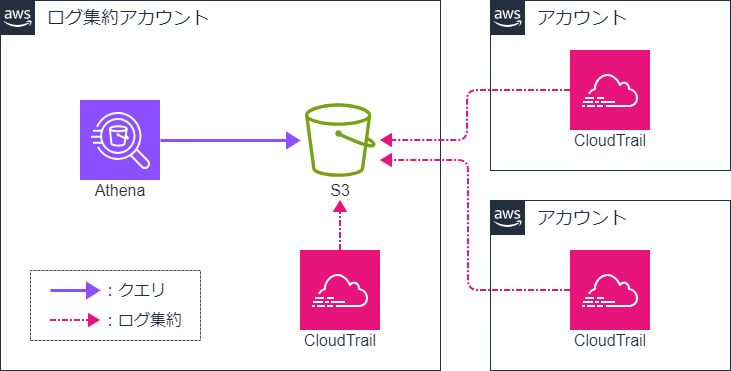
今回はマルチアカウント環境で、ログ集約アカウントに複数AWSアカウントのCloudTrailログを集約していることを前提としております。ログ集約の手順については割愛しますのでご了承ください。構成自体は以下の様にイメージいただければ大丈夫です。
2. 事前準備
クエリ結果の場所を設定する
Athenaでクエリを実行する前に、クエリ実行結果ファイルを出力するS3バケットを準備します。
今回は athena-query-result-[アカウントID] としました。それ以外の設定はデフォルトで問題ないです。
S3バケットを作成したら、Athenaワークグループから出力先として指定します。
クエリエディタを開き「設定」タブから設定してください。

データベースを作成する
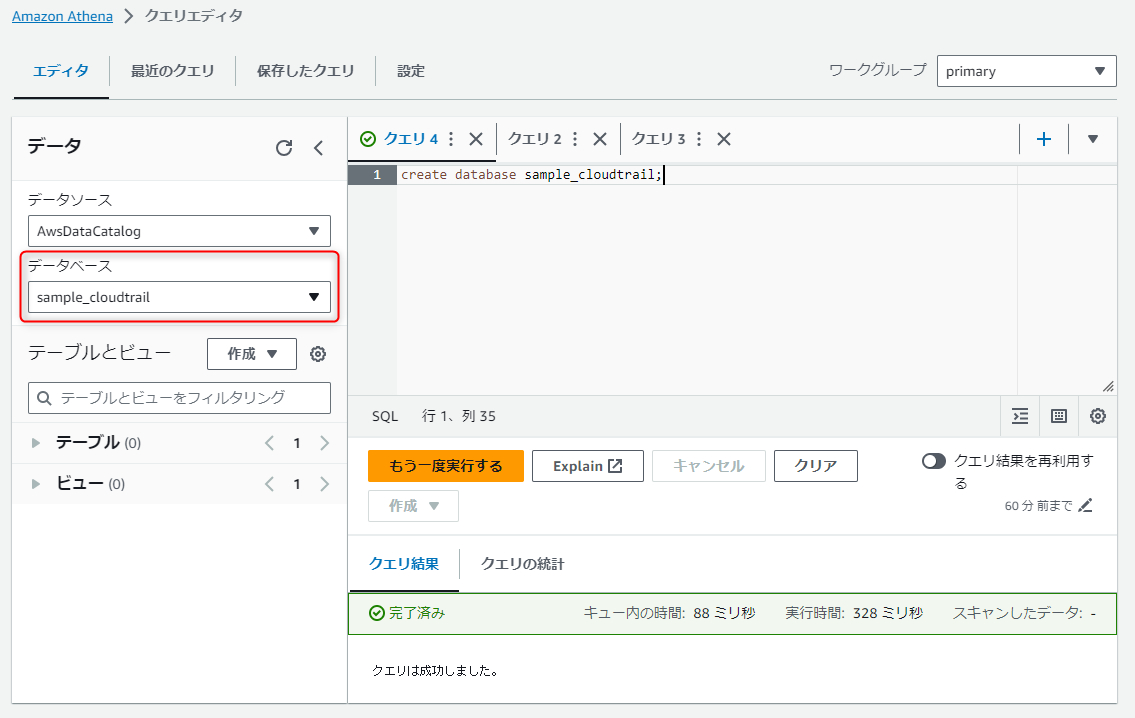
Athenaのクエリエディタに以下を入力して実行し、データベースを作成します。
create database sample_cloudtrail;
クエリが成功したら、「データベース」を作成したものに変更しておきます。クエリで明示的に対象のデータベースを指定しない場合、ここで指定したデータベースに対して実行されます。
3. テーブル作成(パーティション分割なし)
続いてテーブルを作成します。まずは、パーティションを使用せずに作ってみます。
クエリエディタに以下を入力し、実行します。
最終行の [CloudTrail用S3バケット名] と [Organizational ID] は適宜書き換えてください。
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sample_cloudtrail`.`non_partitioned_table` ( `eventversion` string, `useridentity` STRUCT < type: STRING, principalid: STRING, arn: STRING, accountid: STRING, invokedby: STRING, accesskeyid: STRING, userName: STRING, sessioncontext: STRUCT < attributes: STRUCT < mfaauthenticated: STRING, creationdate: STRING >, sessionissuer: STRUCT < type: STRING, principalId: STRING, arn: STRING, accountId: STRING, userName: STRING >, ec2RoleDelivery: string, webIdFederationData: map < string, string > > >, `eventtime` string, `eventsource` string, `eventname` string, `awsregion` string, `sourceipaddress` string, `useragent` string, `errorcode` string, `errormessage` string, `requestparameters` string, `responseelements` string, `additionaleventdata` string, `requestid` string, `eventid` string, `resources` array < STRUCT < arn: STRING, accountid: STRING, type: STRING > >, `eventtype` string, `apiversion` string, `readonly` string, `recipientaccountid` string, `serviceeventdetails` string, `sharedeventid` string, `vpcendpointid` string, `tlsDetails` struct < tlsVersion: string, cipherSuite: string, clientProvidedHostHeader: string > ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'com.amazon.emr.cloudtrail.CloudTrailInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat' LOCATION 's3://[CloudTrail用S3バケット名]/AWSLogs/[Organizational ID]/';
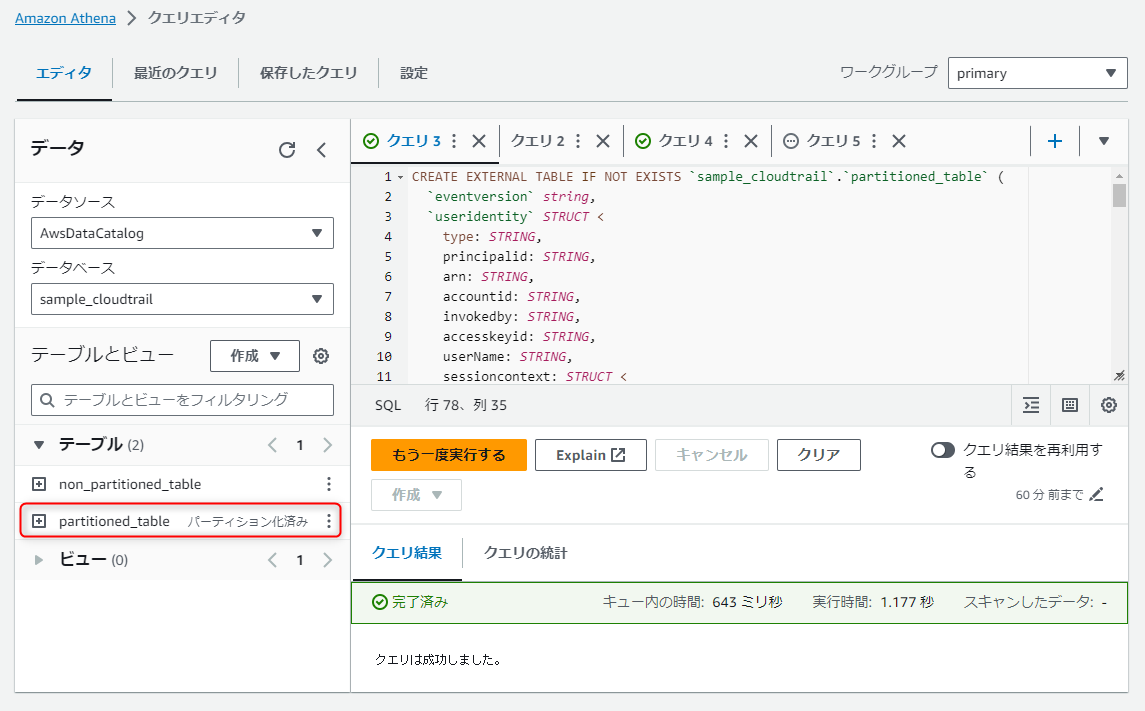
クエリが正常終了すると、テーブルが作成されます。

4. テーブル作成(パーティション分割あり)
今度はAWSアカウントIDとAWSリージョン、日付でパーティション化したテーブルを作成してみます。
組織の証跡を保存するS3バケットは以下の様にパスが切られるため、変数となるこの3つの要素でパーティション化すると汎用的に利用できます。
S3バケット
└ AWSLogs
└ Organization ID
└ AWSアカウントID
└ CloudTrail
└ AWSリージョン
└ 日付 (yyyy/mm/dd)
実行するクエリは以下の通りです。
こちらも、66行と77行の [CloudTrail用S3バケット名] と [Organizational ID] は適宜書き換えてください。
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sample_cloudtrail`.`partitioned_table` ( `eventversion` string, `useridentity` STRUCT < type: STRING, principalid: STRING, arn: STRING, accountid: STRING, invokedby: STRING, accesskeyid: STRING, userName: STRING, sessioncontext: STRUCT < attributes: STRUCT < mfaauthenticated: STRING, creationdate: STRING >, sessionissuer: STRUCT < type: STRING, principalId: STRING, arn: STRING, accountId: STRING, userName: STRING >, ec2RoleDelivery: string, webIdFederationData: map < string, string > > >, `eventtime` string, `eventsource` string, `eventname` string, `awsregion` string, `sourceipaddress` string, `useragent` string, `errorcode` string, `errormessage` string, `requestparameters` string, `responseelements` string, `additionaleventdata` string, `requestid` string, `eventid` string, `resources` array < STRUCT < arn: STRING, accountid: STRING, type: STRING > >, `eventtype` string, `apiversion` string, `readonly` string, `recipientaccountid` string, `serviceeventdetails` string, `sharedeventid` string, `vpcendpointid` string, `tlsDetails` struct < tlsVersion: string, cipherSuite: string, clientProvidedHostHeader: string > ) PARTITIONED BY (region string, date string, accountid string) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'com.amazon.emr.cloudtrail.CloudTrailInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat' LOCATION 's3://[CloudTrail用S3バケット名]/AWSLogs/[Organizational ID]/' TBLPROPERTIES ( 'projection.enabled' = 'true', 'projection.date.type' = 'date', 'projection.date.range' = '2023/01/01,NOW', 'projection.date.format' = 'yyyy/MM/dd', 'projection.date.interval' = '1', 'projection.date.interval.unit' = 'DAYS', 'projection.region.type' = 'enum', 'projection.region.values'='us-east-1,us-east-2,us-west-1,us-west-2,af-south-1,ap-east-1,ap-south-1,ap-northeast-2,ap-southeast-1,ap-southeast-2,ap-northeast-1,ca-central-1,eu-central-1,eu-west-1,eu-west-2,eu-south-1,eu-west-3,eu-north-1,me-south-1,sa-east-1', 'projection.accountid.type' = 'injected', 'storage.location.template' = 's3://[CloudTrail用S3バケット名]/AWSLogs/[Organizational ID]/${accountid}/CloudTrail/${region}/${date}', 'classification'='cloudtrail', 'compressionType'='gzip', 'typeOfData'='file', 'classification'='cloudtrail' );
クエリが正常終了すると、テーブルが作成されます。
5. クエリ実行
それでは、作成した2つのテーブルにクエリを実行してみます。
パーティションなし
以下のクエリを実行します。
IDが xxxxxxxxxxxx のAWSアカウントの東京リージョンで、2023年9月14日に発生したサインインのログを検索します(ちなみにですが当環境では、IAM Identity Center によるシングルサインオンを使用していますので、そのログを取得しています)。
select eventtime as EventTime, useridentity.accountid as AwsAccountId, regexp_extract(useridentity.arn, '([a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,4})', 1) as UserName, useridentity.sessioncontext.sessionissuer.userName as UserRole, responseElements as LoginStatus from non_partitioned_table where eventsource = 'signin.amazonaws.com' and eventname = 'ConsoleLogin' and eventtime >= '2023-09-14T00:00:00Z' and eventtime < '2023-09-15T00:00:00Z' and awsregion = 'ap-northeast-1' and useridentity.accountid = '[AWSアカウントID]';
以下の結果が返ってきました。
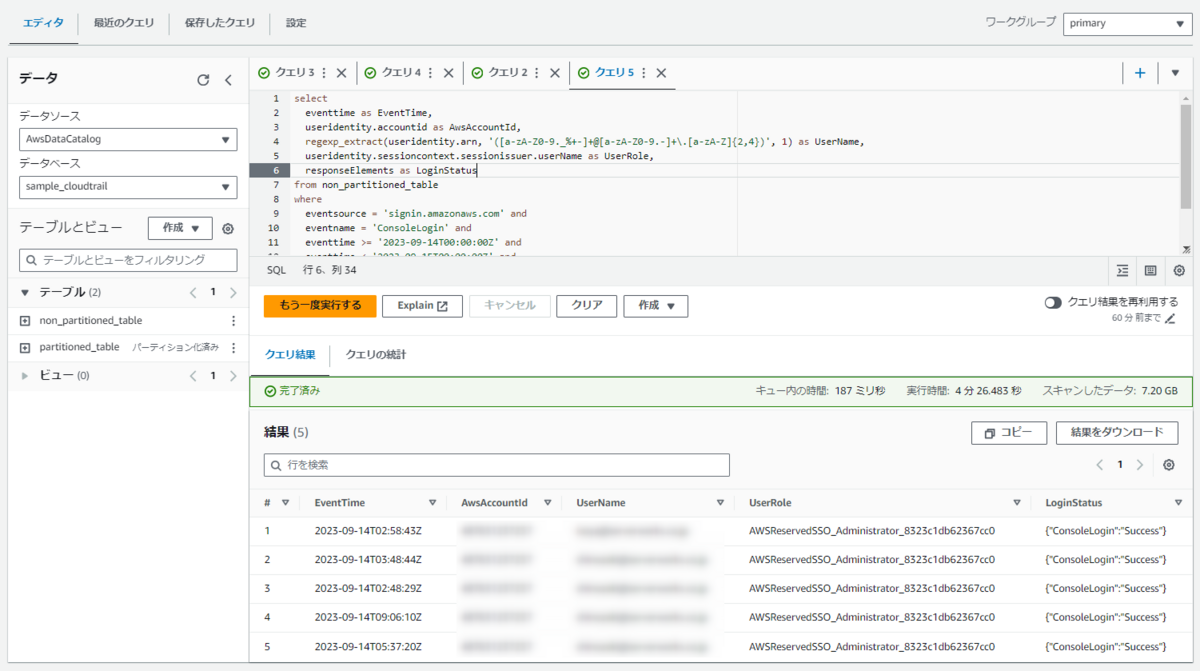
クエリの実行時間は 約4分半、スキャンしたデータ量は 7.20GB となりました。ちなみに実行時のS3バケットのデータ量は 7.4GB でしたので、ほぼ全データがスキャンされたことになります。
Athenaはスキャンしたデータ量に応じた従量課金ですので、S3のデータ量が増えていくにつれ利用料が嵩むことになります(1TBにつき5.00USDの課金)。さらにクエリの実行時間も長くなりストレスフルです。
パーティションあり
以下のクエリを実行します。
WHERE でパーティション化された属性を指定しています。
select eventtime as EventTime, useridentity.accountid as AwsAccountId, regexp_extract(useridentity.arn, '([a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,4})', 1) as UserName, useridentity.sessioncontext.sessionissuer.userName as UserRole, responseElements as LoginStatus from partitioned_table where eventsource = 'signin.amazonaws.com' and eventname = 'ConsoleLogin' and date = '2023/09/14' and region = 'ap-northeast-1' and accountid = '[AWSアカウントID]';
返ってきた結果はパーティションなしのパターンと同じです。ここは期待通りですね。

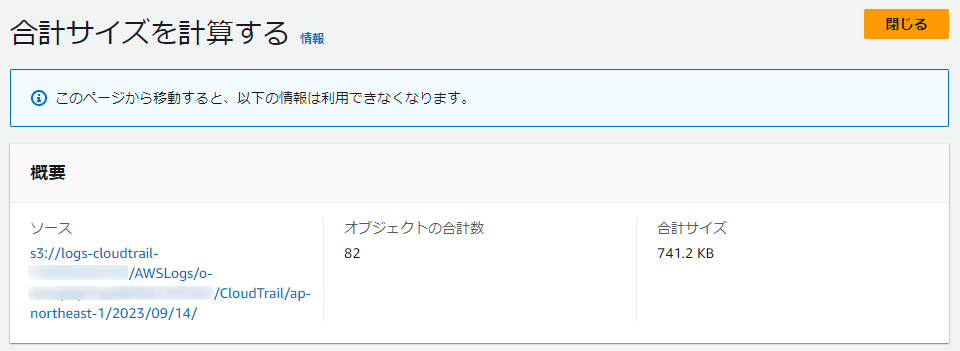
一方、クエリの実行時間は 約0.8秒、スキャンしたデータ量は 741.18KB となりました。スキャン対象がS3バケット全体から一部だけに限定されたため、すさまじく高速になっています。
これでS3のデータが増えていっても、料金や実行時間がネックになることはなさそうです。
ちなみにスキャン対象のパスの合計ファイルサイズと、クエリのスキャンデータ量は一致していました。
6. おまけ
上記のクエリは単一の日付、リージョン、アカウントとしていたので、複数指定の場合の書き方を備忘として残しておきます。
単一の日付でなく、期間で検索したい
以下の様に、date between '[yyyy/mm/dd]' and '[yyyy/mm/dd]' で区間指定が可能です。
select * from partitioned_table where date between '2023/09/14' and '2023/10/27' and region = 'ap-northeast-1' and accountid = '[AWSアカウントID]';
特定のリージョンでなく、複数リージョンで検索したい
以下の様に、region in ('[リージョン名]', '[リージョン名]',) で複数指定が可能です。
全リージョンを対象としたい場合は無指定にすればよいので、region in ~ を行ごと削除しましょう。厳密には「4. テーブル作成(パーティション分割あり)」のクエリの通り、region は 列挙型(enum)で定義していますので、テーブル作成クエリで列挙した全てのリージョンが対象です。
select * from partitioned_table where date = '2023/09/14' and region in ('ap-northeast-1', 'ap-northeast-3', 'us-east-1') and accountid = '[AWSアカウントID]';
利用可能な型については、以下ドキュメントをご参照ください。
特定のAWSアカウントでなく、複数のAWSアカウントで検索したい
リージョンと同様に accountid in ('AWSアカウントID', 'AWSアカウントID') で複数指定が可能です。
ただし、accountid は挿入型(injected)で定義していますので、region と異なり、無指定だとエラーとなる点に注意が必要です。全アカウントを検索対象にしたい場合は、全アカウントのIDを in に渡すようにしてください。
select * from partitioned_table where date = '2023/09/14' and region = 'ap-northeast-1' and accountid in ('[AWSアカウントID]', '[AWSアカウントID]');
7. さいごに
今回はパーティションを使ったAthenaの高速化についてまとめました。
本記事がどなたかの参考になれば幸いです。
松田 渓(記事一覧)
2021年10月入社。散歩が得意です。

